2 January 2021
cpp -- Pointers and Dynamic Memory Management(2)
by Jerry Zhang
Using const with Pointers
A constant pointer points to a constant memory location, but the actual value in the memory location can be changed.
常量指针指向一个不变的内存地址,但这个地址的值可以改变。
double radius = 5;
double* const p = &radius;
如果在指针类型关键字(比如double*)的前面加const,就代表数据也是常量,不可修改。
const double* const pValue = &radius;
Arrays and Pointers
A C++ array name is actually a constant pointer to the first element in the array.
数组的变量名实际上是它的起始地址,数组本质上就是一个指针。
比如:
int list[6] = {11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16};
访问它的每个值, 也可以写成list,(list + 1), *(list + 2), *(list + 3), *(list + 4). 不要忘了加括号。
数组和指针的区别是,数组的地址不能改,比如以下代码是错误的:
int list1[10], list2[10];
list1 = list2; // Wrong
数组实际上是一个常量指针。
Passing Pointer Arguments in a Function Call
A C++ function may have pointer parameters.
前面学了一个函数的参数可以传值,可以传引用。传值是指把变量的值复制一份传给函数,传引用是指给这个变量起个别名传给函数,其实指向的同一个地址。
一个函数还可以传指针。比如:
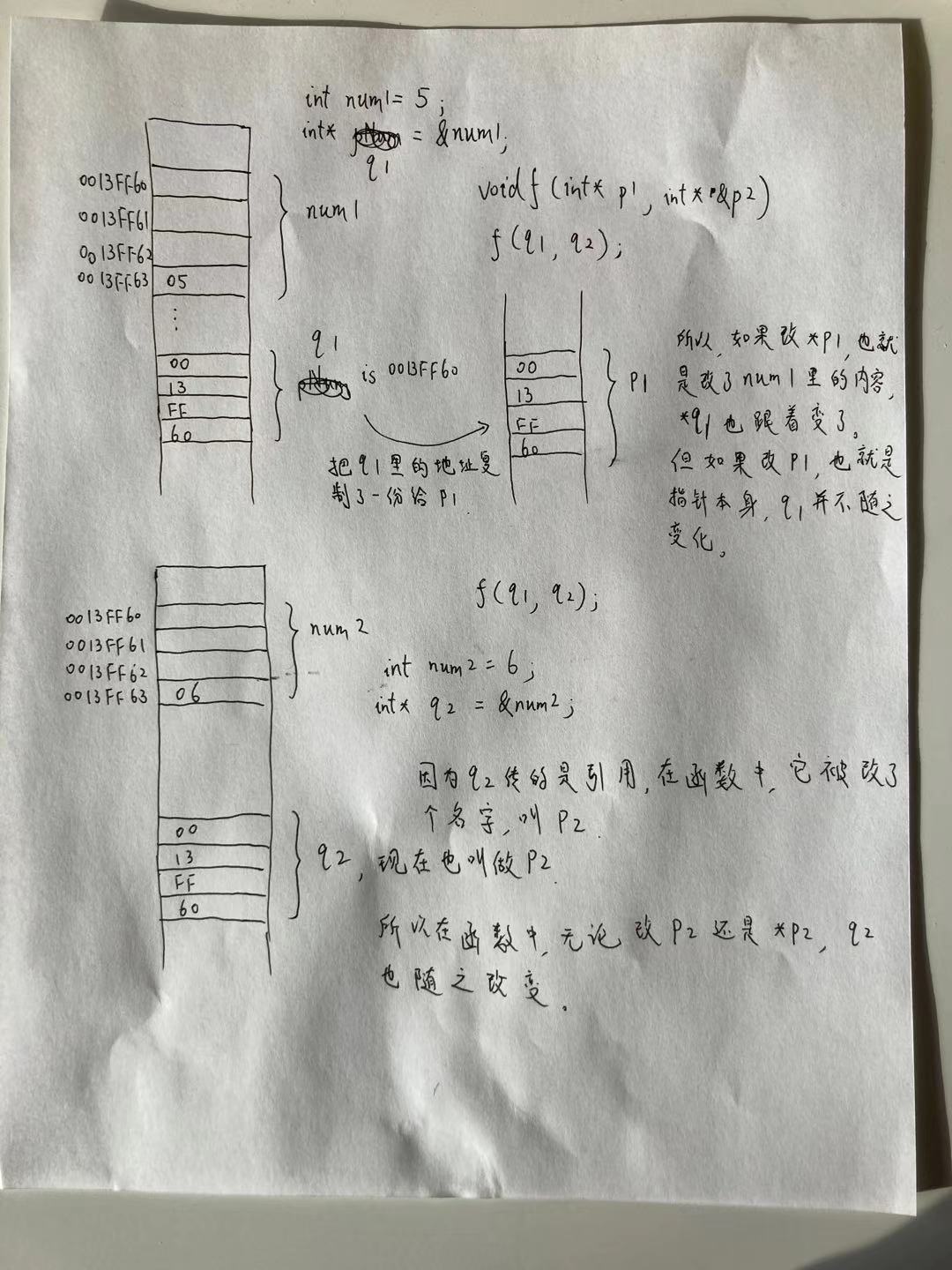
void f(int* p1, int* &p2)
假如我们现在有两个指针q1, q2,传到函数中f(q1, q2)。此时,q1是值传递,q2是引用传递。
-
对于q1来说,我们是把q1这个变量里面的值,也就是某个地址,复制了一份,存到另一个指针p1中,传给函数。此时,p1和q1指向同样的内容,因为它们的地址是一样的。如果在函数中修改了p1(比如,p1 = 20),则*q1也会改变。但是,如果修改的是p1本身,也就是那个地址,q1是不会变的,因为p1只是一份拷贝而已。
-
对于q2来说,我们传的是引用,也就是说,我们给q2起了个别名叫p2传到了函数中。它们本质上是同一个东西。所以如果函数修改了p2,q2也会改变;如果函数修改了p2,q2也会改变。
Useful Array Functions
The min_element, max_element, sort, random_shuffle, and find functions can be used for arrays.
要引入algorithm包:#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void printArray(int* const list, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
cout << list[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int list[] = {4, 2, 3, 6, 5, 1};
printArray(list, 6);
int* min = min_element(list, list + 6);
int* max = max_element(list, list + 6);
cout << "The min value is " << *min << " at index "
<< (min - list) << endl;
cout << "The max value is " << *max << " at index "
<< (max - list) << endl;
random_shuffle(list, list + 6);
printArray(list, 6);
sort(list, list + 6);
printArray(list, 6);
int key = 4;
int* p = find(list, list + 6, key);
if (p != list + 6)
cout << "The value " << *p << " is found at position "
<< (p - list) << endl;
else
cout << "The value " << *p << " is not found" << endl;
return 0;
}
这些函数返回的指针,用星号就能拿到它们的值,比如*min;用这个指针减去这个数组的头指针,就能得到它的index,比如min - list;
另外,这些函数的参数一般是这个数组的起始和结束点的指针,比如,这个数组叫list,那就传进去list和list+6。
Dynamic Persistent Memory Allocation
动态的内存分配,用new关键字
The new operator can be used to create persistent memory at runtime for primitive type values, arrays, and objects.
动态数组的长度可以在runtime时确定:
int* list = new int[size];
new出来的数组会存在heap中,当函数退出时,它不会被销毁,需要用delete手动销毁:
delete [] list;
删除后的指针叫dangling pointers,不要使用*在这些指针上。另外,delete只能用在new出来的指针上。
Memory leak
int* p = new int;
*p = 45;
p = new int;
下图解释了上面三行代码发生了什么:
- (a) 为指针p开了一块长度为4的内存,因为它是一个int
- (b) 通过星号dereference,把那片内存的内容改成了45。
- (c) 在没删除p指针的情况下,直接又给p分配了一块新的内存,导致原来的内存没有任何人可以引用了,造成memory leak.
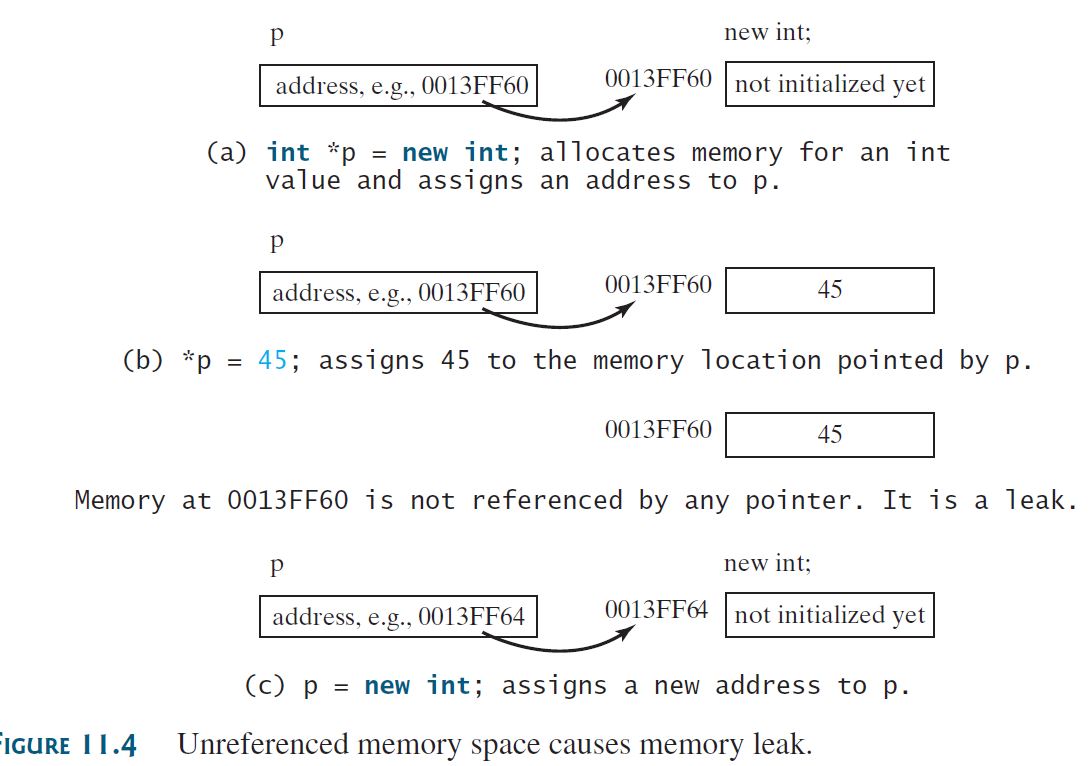
因此,任何时候,都要记得把new出来的东西delete掉。
Creating and Accessing Dynamic Objects
To create an object dynamically, invoke the constructor for the object using the syntax new ClassName(arguments).
ClassName* pObject = new ClassName(); or
ClassName* pObject = new ClassName;
ClassName* pObject = new ClassName(arguments);
例如:
string* p = new string();
string* p = new string("abcdefg");
以前声明对象时,语法是这样的:Circle circle1;或者Circle circle2(5.0);
现在new出来的对象,是一个该类型的指针。所以如果想用它的方法,必须先用星号找到它的内容,再用“点”去调用方法:
string* p = new string("abcdefg");
cout << "The first three characters in the string are "
<< (*p).substr(0, 3) << endl;
cout << "The length of the string is " << (*p).length() << endl;
或者简化的写法是用箭头
cout << "The first three characters in the string are "
<< p->substr(0, 3) << endl;
cout << "The length of the string is " << p->length() << endl;
该对象在程序结束时被删除,也可手动删除。
delete p;
The this Pointer
The this pointer points to the calling object itself.
跟Java用法差不多,但c++的this是个指针,所以要用箭头调用它的实例变量。
this->radius = radius;
Destructors
Every class has a destructor, which is called automatically when an object is deleted.
Constructor前面加一个波浪号,就是destructor。比如,在.h文件中,~Circle();就声明了destructor。
.cpp实现:
Circle::~Circle()
{
numberOfObjects--;
}
You should customize a destructor if the class contains a pointer data field that points to dynamically created memory. Otherwise, the program may have memory leak.
Copy Constructors
For example
Circle(const Circle&)
默认的是shallow copy,所以要自己写一个deep copy,同时别忘了destructor中把所有的指针销毁。
tags: cpp