16 April 2019
JS AJAX
by Jerry Zhang
#Tip of the Day: As a programmer, I finally have my own website, with comments and google analytics. ^_^
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.
- Create an XMLHttpRequest Object
- Send a request to a web server and get the response.
- Execute the response with JavaScript.
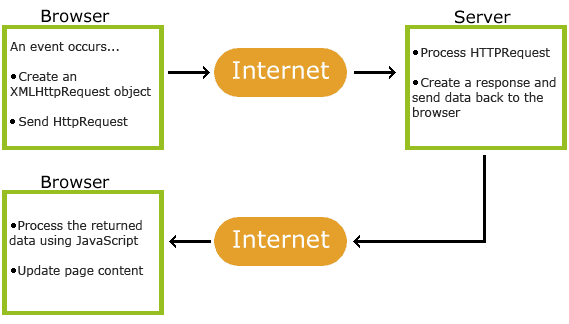
Create an XMLHttpRequest Object and send a GET Request
function loadDoc() {
var xhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhttp.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (this.readyState == 4 && this.status == 200) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML = this.responseText;
}
};
xhttp.open("GET", "ajax_info.txt", true);
xhttp.send();
}
To avoid cached results, add a unique ID to the URL:
xhttp.open("GET", "demo_get.asp?t=" + Math.random(), true);
xhttp.send();
We can also pass some parameters in the request, "demo_get2.asp?fname=Henry&lname=Ford"
POST Requests
xhttp.open("POST", "ajax_test.asp", true);
xhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
xhttp.send("fname=Henry&lname=Ford");
The url parameter of the open() method above, is an address to a file on a server. The third parameter of the open() method is asynchronous or not. It should be set to true.
Synchronous XMLHttpRequest (async = false) is not recommended because the JavaScript will stop executing until the server response is ready. If the server is busy or slow, the application will hang or stop.
onreadystatechange, readyState, and status are all attributes of an XMLHttpRequest object.
tags: AJAX - JavaScript